 Home
Home 
In the field of material testing and engineering, understanding the friction characteristics of various surfaces is paramount. The Dynamic Friction Tester (DFT) is an essential instrument used to measure the sliding friction of materials under dynamic conditions. According to recent industry reports, accurate friction measurements are critical in applications ranging from automotive safety systems to the design of anti-slip surfaces in industrial environments. Studies have highlighted that improper friction testing methodologies can lead to significant performance discrepancies, emphasizing the need for precise and reliable testing practices.
Moreover, a comprehensive analysis by the International Society of Testing Technologies reveals that nearly 30% of testing failures can be attributed to inadequate friction testing procedures. This underscores the importance of utilizing a Dynamic Friction Tester with calibration and methodical testing protocols to ensure consistency and accuracy. As industries continue to push for enhanced safety standards and improved performance, mastering the principles behind the Dynamic Friction Tester is more crucial than ever for engineers and quality control professionals. In this guide, we will explore essential tips and best practices to optimize the use of the Dynamic Friction Tester, ultimately paving the way for accurate and repeatable results.
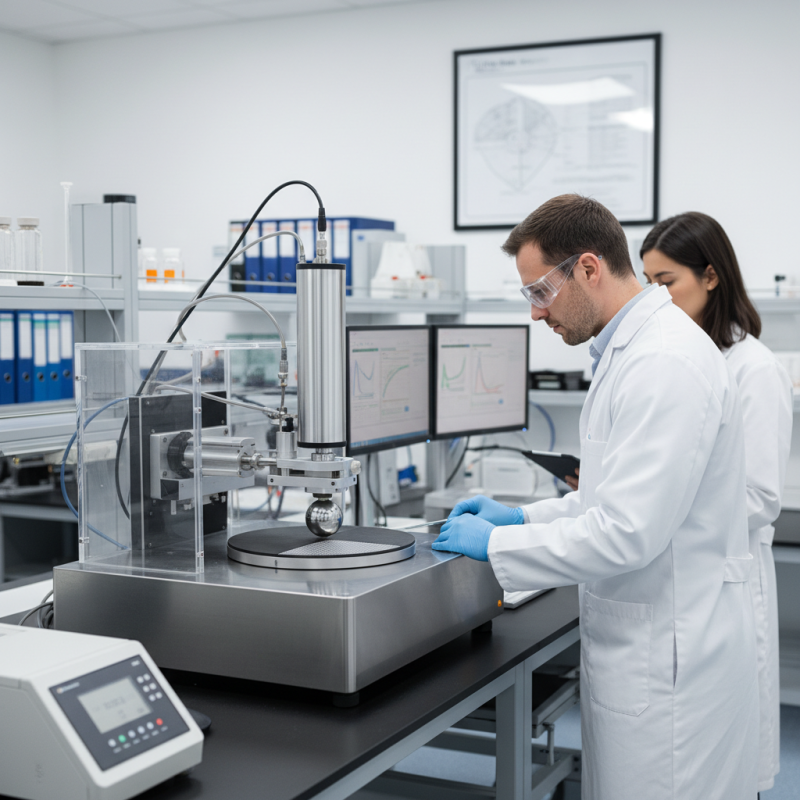

Dynamic friction testing is a crucial method for evaluating the frictional properties of materials under varying conditions. This testing assesses the interaction between surfaces in motion, providing insights into how materials perform during applications such as automotive braking, flooring, and manufacturing processes. According to the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), understanding the dynamic friction coefficient can significantly impact safety and performance metrics, with improper friction levels potentially leading to hazardous failures in mechanical systems.
The principles of dynamic friction testing involve subjecting materials to controlled movements while measuring the resistance encountered. By utilizing devices that simulate real-world conditions, engineers can acquire data that reflects the material's behavior in action. A study published in the Journal of Materials Science showed that variations in temperature and surface roughness have significant effects on dynamic friction coefficients, highlighting the importance of replicating environmental factors during testing.
The results from these tests are essential for industries such as automotive and construction, where precise friction characteristics are necessary for quality assurance and compliance with safety standards.
Dynamic friction testers are essential instruments for evaluating the frictional characteristics of various surfaces. Understanding the key components of these testers is crucial for achieving accurate and reliable results. The primary components include the loading mechanism, displacement sensor, and the control unit. The loading mechanism applies a predetermined force on the test surface, while the displacement sensor tracks the movement and interaction between surfaces during testing. Together, these elements work to measure dynamic friction, ensuring a thorough analysis of material performance.
Another important component is the data acquisition system, which captures and processes the test results in real time. This system plays a pivotal role in analyzing the dynamic friction data, allowing for the interpretation of results under various conditions. Additionally, the environmental chamber can be used to simulate different humidity and temperature levels, further enhancing the accuracy of the results. Careful attention to the calibration of these components is vital, as even minor discrepancies can significantly affect the testing outcome. Understanding these elements will enable effective use of the dynamic friction tester and promote better material selection and quality control in various applications.
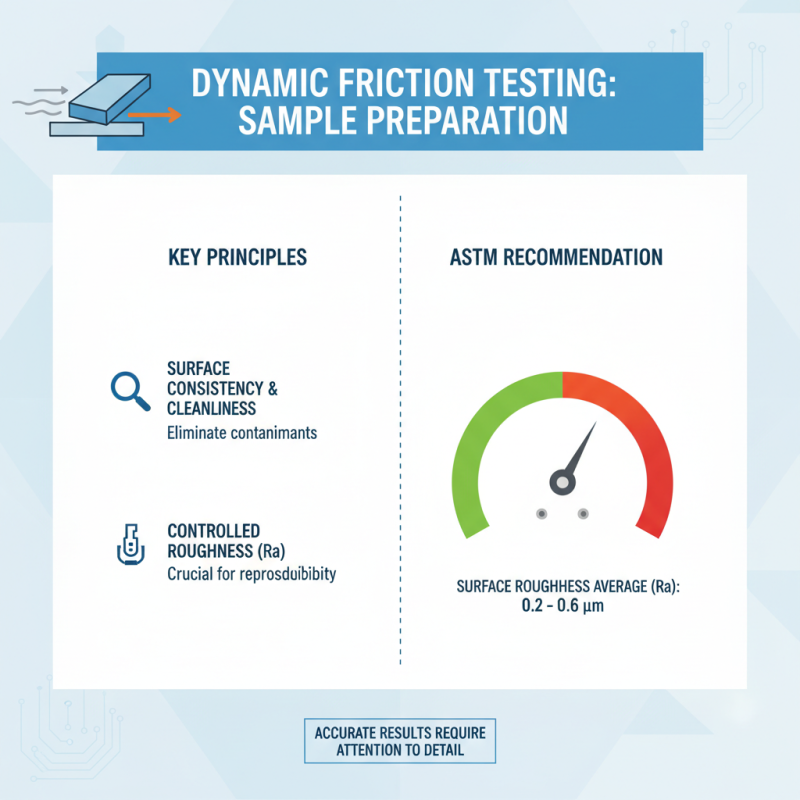
When preparing samples for dynamic friction testing, attention to detail can significantly impact the accuracy of the results. It is essential to ensure that the sample’s surface is consistent and free of contaminants. According to the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), surface roughness plays a crucial role in friction measurements; controlling this parameter is vital for replicating test conditions and obtaining reliable data. Specifically, maintaining a surface roughness average (Ra) of around 0.2 to 0.6 micrometers is often recommended to ensure reproducibility and precision in friction results.
Additionally, environmental factors such as temperature and humidity should be carefully monitored during sample preparation. A study published by the International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing emphasized that variations in ambient conditions can lead to discrepancies in test outcomes. For instance, a temperature increase of just a few degrees can alter the material properties, leading to significant variations in the friction coefficient. To mitigate these effects, it is advisable to conduct tests in a controlled laboratory environment, ensuring that samples are acclimated to the testing conditions for at least 24 hours before testing. Following these best practices will help in achieving consistent and accurate results in dynamic friction testing.
Interpreting results from dynamic friction tests is essential for understanding material performance under various conditions. These tests yield data that can reveal critical insights into how surfaces interact, how wear occurs, and how lubrication affects dynamic friction. When analyzing your results, look for patterns in friction coefficients across different speeds and loads. A consistent coefficient may indicate stable material performance, while significant fluctuations could suggest underlying issues that need addressing.
Tips for accurate data analysis include ensuring your test setup is standardized for each run. Consistency in environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, can significantly influence your results. Additionally, consider replicating tests multiple times to account for variability and enhance the reliability of your data. Make use of statistical tools to evaluate your results effectively; this can help you identify outliers and trends that might inform further experimentation.
Another crucial aspect of data interpretation is understanding the limitations of your materials and their interactions. Not all materials will behave the same under dynamic conditions, and surface treatments or contaminants can significantly impact results. By correlating your dynamic friction data with material properties and test conditions, you can derive a more comprehensive understanding of performance characteristics that can guide future applications or developments.
| Test Sample | Material Type | Surface Texture | Dynamic Friction Coefficient | Environmental Conditions | Test Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample A | Rubber | Smooth | 0.45 | 25°C, 50% Humidity | 2023-10-01 |
| Sample B | Plastic | Textured | 0.32 | 20°C, 30% Humidity | 2023-10-02 |
| Sample C | Metal | Rough | 0.50 | 30°C, 60% Humidity | 2023-10-03 |
| Sample D | Composite | Mixed | 0.38 | 22°C, 40% Humidity | 2023-10-04 |
Dynamic friction testing is essential for evaluating the performance of materials used in various applications. However, there are several common pitfalls that can undermine the accuracy of test results. One major issue arises from inadequate surface preparation. A clean, well-maintained testing surface is crucial; any contaminants or debris can lead to inaccurate measurements. Ensuring that both the test specimens and the testing apparatus are free from dirt and oils can significantly enhance the reliability of the results.
Another area to watch for is maintaining consistent testing conditions. Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity can affect friction measurements. It’s advisable to conduct tests in a controlled environment whenever possible. Additionally, using a consistent testing speed can help provide uniform results, as variations in speed can lead to fluctuations in friction readings.
For better accuracy, consider implementing these tips: First, always calibrate your equipment before starting tests to ensure precision. Second, document every test's environmental conditions to identify any potential influences on the data. Lastly, conduct multiple trials and average the results to minimize random variations. By addressing these common pitfalls and following tips for best practices, you can enhance the accuracy of your dynamic friction testing procedures.











